Many people are interested in the question of the appearance of worm eggs, since infection with parasites is not uncommon. Infection usually occurs when worm eggs enter the human body. This can happen through dirty hands, food, and contact with feces and pet hair. If a parasite infection is suspected, a person tries to independently detect worm eggs in the feces. However, the eggs cannot be seen with the naked eye, they are microscopic in size and can only be detected when analyzing the feces.
Roundworm infection
Fungal infection occurs when eating unwashed vegetables and fruits, poorly cooked meat and fish. Infection through contaminated hands is possible, especially in children. The worm's habitat is the human intestine
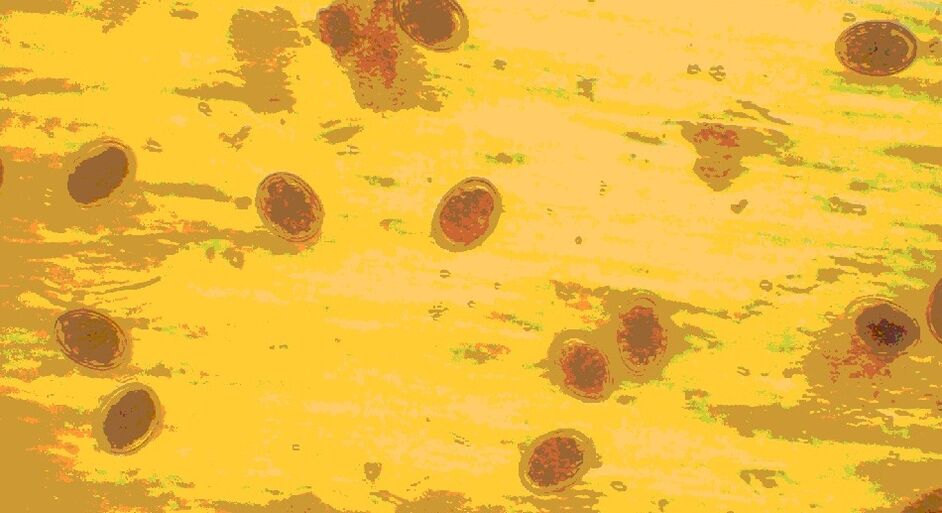
Ascaris eggs can only be seen under a microscope. Their size is very small (about 0. 07 mm). Adult worms are also very difficult to see in the feces. The particles of the dead worms are removed from the intestines only after taking anthelmintic drugs. They look like translucent, elongated inclusions.
Only a microscopic examination of the feces helps determine the presence of roundworm eggs. Eggs are yellow formations with a shell covered with tubercles. Sometimes an embryo can be seen in fertilized eggs. They are highly resistant to environmental influences and can exist outside the human body for years.
Ascaris eggs
Since it is very difficult to detect traces of roundworms in the body, you should be aware of the symptoms of invasion: a sudden increase in body temperature;
- skin rashes;
- choking and coughing (sometimes with blood);
- muscle spasms;
- joint pain.
These manifestations are associated with the effect of the roundworm allergen on the body. If such symptoms are observed, a stool test should be performed for worm eggs.
Where should you go if you suspect worms?
If you suspect a helminthic infection, you should make an appointment with an infectious disease specialist. In the early stages of helminthiasis, there are no specific symptoms, so it is quite difficult to suspect that you or a loved one have worms. In general, the patient complains of mild malaise: indigestion, headache, apathy.
If the symptoms do not go away within a week, or if the condition returns periodically (for example, you feel sick once every 3-4 months), consult your doctor. Attacks of poor health are associated with the migration of parasites.
Pinworm infection
A fungal infection can be contracted through casual contact with a sick person (through shared objects, shaking hands). Humans are often infected by cats and dogs; worm eggs live on the fur of pets. Children are particularly susceptible to this disease. A child can become infected with these parasites in kindergarten or from animals. Worm eggs can be found on any object with which the patient has come into contact. They can be found under fingernails, on toys, bedding and underwear. Therefore, it is very easy to get infected with pinworms.
Pinworm eggs
Pinworms lead to the development of a disease called enterobiasis. Signs of infection include:
- itching in the area of the anus;
- diarrhea;
- nausea;
- sudden weight loss;
- bloating.
Worm eggs are not excreted in the faeces. The parasites multiply in the anal area, where they lay eggs, which causes itching. In order to detect the presence of these worms in the body, the skin of the anus is scraped and the removed material is subjected to microscopic examination. Such an analysis is usually required when a child is enrolled in kindergarten. The scraping should be done in the morning, before washing the child, so that the parasite eggs are not washed away. Perform triplicate analysis over several days. Fungal eggs look like elongated white cereal particles under a microscope.
Adult fungi can be found in the feces of children and adults. Small, about 0. 5-1 cm long, white worms, one end of their body is pointed.
Folk remedies against helminths
In the case of diphyllobothriasis, folk remedies should only be used after consultation with a doctor. They cannot replace drug treatment, they can only complement it. The most commonly used recipe is pumpkin seeds.
Pumpkin seeds have a harmful effect on many worms, including tapeworms. They contain cucurbitin, a substance that kills parasites. The seeds are ground with a coffee grinder or blender, then diluted with water to a paste. For adults, you will need 300 g of seeds, and for children, 50-100 g. The prepared product is consumed in the morning on an empty stomach for 1 hour. After that, you should not eat breakfast. After 3 hours, a laxative should be taken, and after another 30 minutes, an enema.
When the parasite leaves the stool, it should be examined. You have to pay attention to whether there is a head at one end of the body. If it is not there, it means that only the segments have come out and the parasite will be able to regrow the body and release the eggs. In this case, the treatment must be repeated.
Whipworms
This type of parasite is quite rare in the central zone of our country. Whipworms often live in southern regions, as the eggs of this worm like warmth. Most infections are observed in rural areas.
Whipworm eggs live in the soil. Infection occurs through hands, contaminated soil particles, and poorly washed vegetables and fruits.
As a result of the infection, a disease occurs - trichocephalosis. The whipworm is a parasite in the intestines. This worm causes anemia as it feeds on human blood and causes severe abdominal pain.
Whipworm eggs
The eggs of the parasite are excreted in the feces, but they are very small and cannot always be seen even under a microscope. Eggs can only be detected with a stool test in the case of a very severe infection. They are barrel-shaped and brownish-yellow in color. The egg has holes on both sides.
What do worms look like in stool? It is very difficult to detect them alive in the feces, since whipworms cannot live long outside the human body. Only with anthelmintic therapy can you detect dead white worms in the stool.
To diagnose trichuriasis, the rectum and sigmoid colon are examined with a special device (sigmoidoscopy). In this way, the accumulation of parasites in the intestines can be detected. Treatment of the infection takes a long time, as the whipworm eggs are protected by a thick shell.
Diagnosis of helminthiasis
Many helminth infections are diagnosed with a stool test first. If you find black dots in your stool or white worms in your stool, this test should be done as soon as possible.
However, it is not only black speckled stools that indicate coprogram. Often, even eggs that are invisible to the eye can be easily identified under a microscope. A more accurate diagnosis of feces is made by detecting helminth DNA particles using the PCR technique.
If a person has many black spots in their stool, other diagnostic methods include:
- Scraping from the area near the anus;
- Blood test by ELISA, PCR, RNGA and other methods;
- Be sure to get blood chemistry and CBC;
- In order to identify the localization of parasites, ultrasound, MRI and CT are performed in some cases;
- To diagnose the migration stage of helminths, an X-ray examination is required.
In certain forms of helminthiasis, the contents of the sputum, rectal mucosa, urine and gall bladder can be tested. Sometimes an endoscopy is used for diagnosis.
Trichinella
This is one of the most dangerous types of roundworms. Trichinella parasitizes human muscles. Severe infection sometimes leads to death.
Trichinella enters the body by eating poorly processed meat from wild and domestic animals. Worms are only killed at very high temperatures (around 80°C). Worms can be found in salted or smoked meat, such treatment does not destroy their larvae.
Possible contamination from undercooked meat
Parasite eggs cannot be detected in the human body. The female trichinella carries the eggs in her body, and then the larva is born. These are worms that reproduce ovoviviparously. Trichinella cannot be detected in the stool. The newborn larvae immediately enter the blood and lymph, bypassing the intestines. The larvae die quickly in the faeces.
Usually, the disease is diagnosed when the parasite has managed to get into the muscles. In this case, the person is bothered by the following symptoms: muscle pain;
- swelling;
- febrile state (high temperature, pain, malaise);
- irregular bowel movements with constipation or diarrhea.
A blood test with a serological test is performed to detect the invasion. This is the only method to detect trichinella in the body.
Article for people suffering from a disease diagnosed by a doctor. It is not a substitute for a doctor's prescription and cannot be used for self-diagnosis.
Broad tapeworm
The human body contains only immature tapeworm eggs. They are excreted in the faeces and enter the external environment. With untreated sewage, the eggs end up in bodies of water, where they begin their development. First, they enter the body of freshwater crustaceans. Fish from reservoirs become infected with tapeworms when they eat small crustaceans. And a person gets a worm infection when he eats poorly cooked, infected freshwater fish or raw pike caviar.
Broad tapeworm eggs
The disease diphyllobothriasis occurs, which manifests itself in the following symptoms: pain in the abdominal cavity;
- nausea and vomiting;
- intestinal problems (constipation or diarrhea);
- loss of appetite or excessive hunger.
What do helminths in the class of tapeworms look like? It is a large parasite that can reach 10 m in length. Only some living parts (segments) of the worm are found in the feces, they look like long (from 30 cm to 3 m) white ribbons. It should be removed from the stool with tweezers, transferred to a clean container, and taken to a parasitologist or infectious disease specialist for analysis.
Microscopic examination of stool can detect tapeworm eggs. Their size is about 0. 07 mm. Eggs appear as yellowish oval-shaped formations covered with a thick shell. Cover one end of the egg with a cap and the other end with a bump.
Worm larvae can be passed in the feces, but they are not dangerous. Diphyllobothriasis cannot be contracted from an infected person or animal. Infection occurs only through consumption of fish.
Damage to the body
When a broad tapeworm enters the intestines, the disease diphyllobothriasis develops. Helminths mainly affect the gastrointestinal tract. Inflammation and ulcers form on the intestinal walls where the worm attaches. If there is not one, but several parasites in the body, they can clog the lumen of the intestine, resulting in an obstruction. The helminth constantly irritates the walls of the gastrointestinal tract, which leads to disruption of digestive processes. In addition, it poisons the human body with waste products, which causes allergies. If the parasite remains in the body for a long time, severe anemia and vitamin B12 deficiency develop.
Cattle and pig tapeworm
Humans become infected with this type of parasite by eating poorly processed meat from domestic animals. The worm segments are excreted in the patient's feces. In the external environment, the segments move through the soil and lay eggs, which contain larvae. These eggs are then ingested by pets. When a person eats contaminated beef or pork, they become infected with bovine or porcine tapeworms. Meat must be boiled or fried for at least 30 minutes to kill tapeworms.
Bull tapeworm
The cattle tapeworm causes taeniahrynchiasis, the pig tapeworm causes taeniasis. The symptoms of these diseases are similar: abdominal pain;
- constant feeling of hunger;
- nausea and vomiting;
- weakness;
- weight loss;
- diarrhea;
- itching in the anal area when the segments come out.
The worms in the patient's stool are in the form of segments. They look like light streaks about 1-2 cm long. Pig tapeworm segments are longer and consist of 3 segments.
When analyzing the feces, tapeworm eggs (oncospheres) are detected. These are round formations with a dense shell, inside which there is an embryo.
Infection with pig tapeworm is possible with dirty hands, without an intermediate host. The segments excreted in the patient's excrement are dangerous. They can enter the human body from contaminated soil. In this case, the larvae of the pig tapeworm multiply in the human body and cause a serious disease - cysticercosis. This is a very dangerous invasion. The larvae enter the brain, spinal cord, eyes, heart and lungs, causing severe damage. In case of cysticercosis, the segments and eggs are not excreted in the stool. The disease can only be detected by serological blood tests and cerebrospinal fluid analysis.
Classification
Modern medicine classifies worms that live in the human body as follows: Luminal. Such worms live in the lumen of the intestine. These include broad tapeworms, dwarf and bull tapeworms, hookworms, scoopworms, whipworms, roundworms, etc.
Fabric. Such worms choose muscle and lung tissue, as well as organs such as the pancreas, liver, brain, etc.
Depending on exactly where the tissue helminths are located, the invasion may have the following names:
- Filariasis. The parasites live in the lymph nodes
- Cysticercosis. The area of the brain affected by helminths
- Echinococcosis. Helminthic infection is diagnosed in the liver
- Paragonimiasis. The parasites live in the lungs
Flukes
Among the worms belonging to the class of flukes, the cat fluke (liver fluke) occurs most often in humans. The habitat of worm eggs is fresh water. From there, the parasite enters the body of the shellfish and then the fish. Cats and humans become infected with fluke by eating poorly processed freshwater fish and through contaminated water. A sick cat does not pose a danger to humans.
Burbot with liver parasites
Most often, fish belonging to the carp family are infected. Salting or smoking does not lead to the death of the parasite. A fairly long heat treatment of the product is required. You can become infected with fluke by accidentally swallowing water from a lake or river. There are known cases of invasion after watering the beds with contaminated water.
Feline distemper attacks the liver. There is pain in the right side of the abdominal cavity, nausea, vomiting, fever. During the medical examination, an enlargement of the organ is detected.
Adult worms are not excreted in the faeces. What do fluke eggs look like under a microscope? When examining the stool, you can see transparent ovals with a golden skin. One side of the egg has a plug that opens when the larva hatches. For diagnostic purposes, a blood test to detect antibodies or an enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay is performed.
How do you know if you have worms?
It is impossible to independently determine the presence of helminthic infection. In the initial stage, the disease can be practically asymptomatic. The patient does not feel pain, the immune system is able to suppress the pathogenic effect of toxins and allergens for a while. Usually, the aggravation begins during the period of larval migration or when the number of worms increases. The stronger the infection (i. e. the more parasites), the more symptoms appear.
However, the asymptomatic course of the invasion is dangerous - the patient infects others and his health gradually deteriorates. In order to detect the disease, a preventive examination must be carried out at regular intervals in the hospital. As part of prevention, the therapist prescribes an examination for worms at least once a year. If you live in an endemic region - once every six months.
What can be seen with the naked eye?
Since some parasites are very small, it is not always possible to detect their presence in the body just by the presence of eggs in the feces. Some parasites are microscopic in size and live hidden in the body without revealing their presence. In addition, they are not always localized in the intestines and can migrate throughout the body. Therefore, for the diagnosis of parasitic infections, serological tests are performed, which are based on the antigen-antibody immune reaction.
Each parasite looks different, has its own specific development cycle, symptoms of infection and treatment regimens are different. However, there are several symptoms that may indicate a parasitic infection in a person:
- rapid weight loss;
- intestinal disorder: diarrhea replaces constipation;
- intense itching in the anus;
- skin rashes of unknown etiology;
- abdominal pain;
- bloating;
- loss of appetite;
- inexplicable craving for sweets;
- sometimes uncontrollable appetite in adults;
- frequent colds due to a decrease in the body's defenses.